A heart physical examination is a crucial step in evaluating a person’s cardiovascular health. Doctors use various techniques in a heart physical examination to detect signs of heart disease or abnormalities.
Conducting regular physical examinations of the heart allows for the early identification of risks associated with cardiovascular disease.
Procedures performed by medical professionals can provide valuable information about the function and condition of the patient’s heart. Learn in detail about the four main procedures in a heart physical examination that you need to know.
What is a Heart Physical Examination?
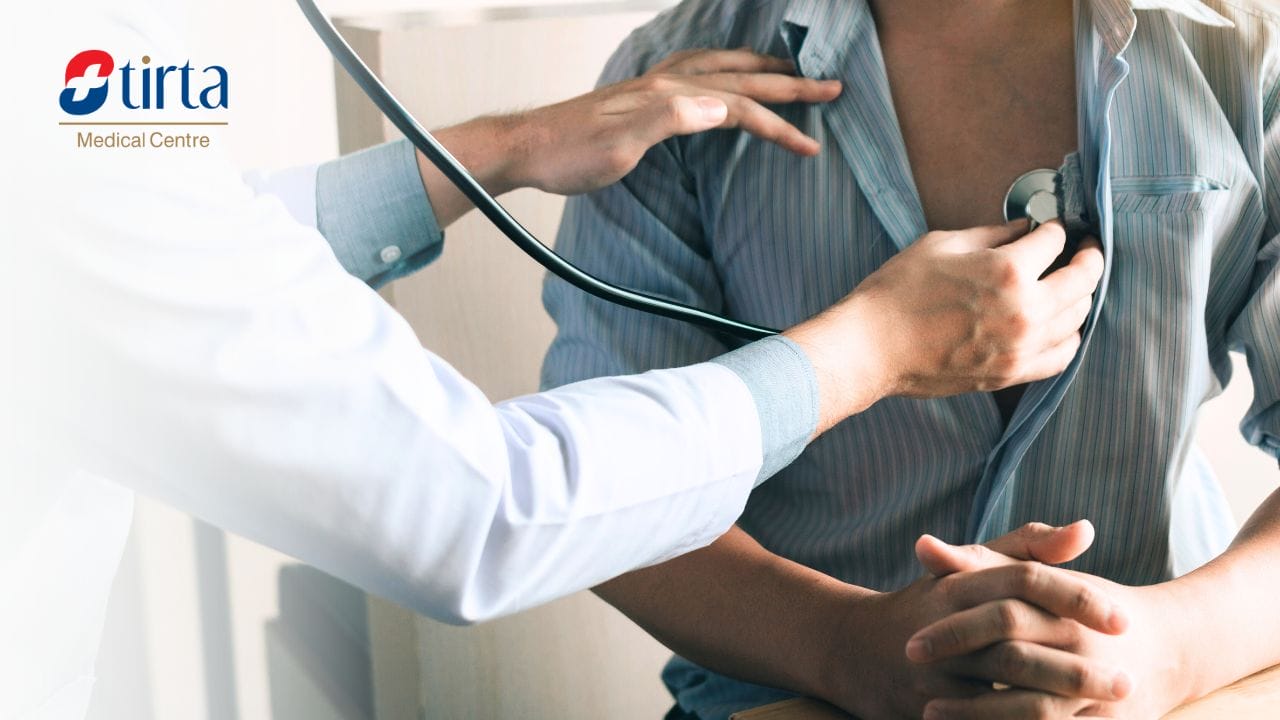
A heart physical examination is a set of procedures done by a doctor to assess a patient’s heart health and function through inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation. This exam is crucial for a complete cardiovascular assessment, offering valuable insights into the heart’s structure and function, as well as the vascular system.
During a heart exam, the doctor will check the patient’s chest by observing, feeling, tapping, and listening for signs of heart issues. This procedure is typically performed alongside a detailed medical history and assessment of vital signs like blood pressure, pulse, and respiratory rate.
Purpose of Heart Physical Examination
The heart physical examination serves several main purposes, including:
- Detecting abnormalities in heart structure and function
- Evaluating heart rate and rhythm
- Identifying signs of heart disease such as murmurs or abnormal heart sounds
- Assessing tissue perfusion and peripheral circulation
- Detecting signs of heart failure, such as edema or jugular vein distension
- Aiding in the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease
- Monitoring the progress of previously diagnosed heart disease
- Determining the need for further examinations like ECG or echocardiography
By carefully performing a heart physical examination, doctors can obtain crucial information to determine the next diagnostic and therapeutic steps for patients with cardiovascular complaints.
Heart Physical Examination Procedures
The heart physical examination consists of 4 main procedures performed systematically and thoroughly by the doctor:
1. Inspection
The doctor will visually observe the patient’s chest, looking for signs of abnormalities such as chest deformities, abnormal pulsations, or jugular vein distension. Inspection also includes assessing skin color, breathing patterns, and signs of peripheral edema.
2. Palpation
At this stage, the doctor will use their hands to feel the heartbeat (ictus cordis), vibrations (thrill), and assess the characteristics of the pulse. Palpation is also performed to detect any tenderness or abnormal masses in the precordial area. The doctor will note the location, amplitude, and duration of the apical impulse.
3. Percussion
The doctor will tap the patient’s chest with fingers to assess the heart’s boundaries and detect conditions such as cardiomegaly or pericardial effusion. Percussion can also help identify fluid in the pleural cavity, which may affect the heart examination.
4. Auscultation
This procedure is the most crucial part of the heart physical examination. The doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to heart sounds at several different auscultation areas. Auscultation is performed to assess heart rhythm, the intensity of heart sounds, and the presence of additional sounds such as murmurs, gallops, or friction rubs.
The doctor will carefully listen to the first (S1) and second (S2) heart sounds and the possible presence of a third (S3) or fourth (S4) heart sound. During auscultation, the doctor may ask the patient to breathe normally, hold their breath, or perform the Valsalva maneuver to evaluate changes in heart sounds.
These four procedures are performed in sequence and integrated to provide a comprehensive picture of the patient’s heart condition. The results of the heart physical examination are then integrated with findings from the history and vital signs examination to determine the diagnosis and follow-up plan.
It’s important to note that a heart physical examination requires adequate clinical skills and experience. Doctors must be able to accurately interpret findings and correlate them with symptoms and medical history.
In some cases, the heart physical examination may need to be supplemented with supportive examinations such as an electrocardiogram (EKG) or echocardiography to confirm the diagnosis.
Preparation Before Examination
Before undergoing a heart physical examination, there are several things that patients need to consider:
- Wear clothing that can be easily opened at the chest area.
- Inform the doctor about any medical history and medications currently being taken.
- Report any current complaints or symptoms.
- Avoid heavy physical activity or caffeine consumption a few hours before the examination.
- Stay relaxed and breathe normally during the examination.
Proper preparation will help ensure accurate examination results and facilitate the doctor’s evaluation.
Further Recommendations After Heart Physical Examination
Based on the results of the heart physical examination, the doctor may provide several further recommendations:
- Additional tests such as EKG, echocardiography, heart stress test, chest X-ray, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), or heart CT scan.
- Consultation with a heart specialist for further evaluation.
- Lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet and regular exercise.
- Medications to address any abnormalities found.
- Regular monitoring to evaluate the progression of heart condition.
- Patient education about heart disease risk factors and prevention methods.
These recommendations will be tailored to each patient’s condition and specific findings from the heart physical examination.
When is a Heart Physical Examination Needed?
A heart physical examination is recommended in several situations:
- Presence of characteristics of heart disease such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations.
- Routine screening for patients with heart disease risk factors.
- Pre-operative evaluation for patients about to undergo surgery.
- Monitoring for patients with a history of heart disease.
- Heart fitness assessment before starting an intensive exercise program.
- Evaluation of patients with congenital abnormalities that may affect the heart.
To receive a comprehensive and accurate heart physical examination, you can visit Tirta Medical Centre (TMC). Tirta Medical Centre, a top healthcare provider in Indonesia, offers heart exams performed by skilled specialists using advanced medical equipment.
The commitment to quality service and medical staff expertise makes TMC a top choice for heart examinations in Indonesia. Regular check-ups and adhering to your doctor’s advice are essential for maintaining heart health and preventing future cardiovascular issues.
References:
- Skills Lab, Faculty of Medicine, UNS. Accessed in 2024. Breast and Advanced Cardiovascular Examination: Advanced Cardiovascular Examination: https://skillslab.fk.uns.ac.id/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/smt-4-Pemeriksaan-kardiovaskuler-lanjut-2019.pdf
- Ministry of Health (Kemenkes). Accessed in 2024. Cardiovascular Support Examination: https://ayosehat.kemkes.go.id/pemeriksaan-penunjang-kardiovaskular
- NCBI. Accessed in 2024. Cardiac Exam: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553078/
- MSD Manual Professional Edition. Accessed in 2024. Cardiovascular Examination – Cardiovascular Disorders: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/cardiovascular-disorders/approach-to-the-cardiac-patient/cardiovascular-examination
- UC San Diego School of Medicine. Accessed in 2024. Cardiovascular Exam: https://meded.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.html
- NHS. Accessed in 2024. Cardiovascular Disease: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/cardiovascular-disease/
- CDC. Accessed in 2024. Preventing Heart Disease: https://www.cdc.gov/heart-disease/prevention/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/prevention.htm
- Healthline. Accessed in 2024. How Is Heart Disease Diagnosed?: https://www.healthline.com/health/heart-disease/tests-diagnosis
- WebMD. Accessed in 2024. Heart Disease: Tests & Diagnosis: https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/guide-chapter-heart-disease-tests-diagnosis
- Mayo Clinic. Accessed in 2024. Heart Disease – Diagnosis and Treatment: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353124
- King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Accessed in 2024. Cardiac Non-Invasive Diagnostics: https://www.kch.nhs.uk/services/services-a-to-z/cardiac-non-invasive-diagnostics/