Coronary heart disease is one of the most common and dangerous cardiovascular diseases. It can be life-threatening if not properly managed. Gain a comprehensive understanding of coronary heart disease, from its definition and causes to its symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
What Is Coronary Heart Disease?
Coronary heart disease, or coronary artery disease (CAD), happens when the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart become damaged or narrowed.
The narrowing is due to plaque buildup, made of cholesterol and other substances, on the coronary artery walls, a condition called atherosclerosis.
Narrowed coronary arteries restrict blood flow, limiting the nutrients and oxygen that reach the heart muscle. This can cause various health problems, ranging from chest pain (angina) to heart attacks.
Causes of Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary heart disease is caused by atherosclerosis, which is the accumulation of plaque on the walls of the coronary arteries. This plaque consists of cholesterol, fats, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, the plaque can harden and narrow the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
It’s important for you to be aware of several factors that contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and CAD:
1. Dyslipidemia
High LDL cholesterol and low HDL cholesterol levels in the blood.
2. Hypertension
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage artery walls.
3. Diabetes mellitus
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels.
4. Smoking
Chemicals in cigarettes can damage the walls of blood vessels and increase the risk of plaque formation.
5. Chronic inflammation
Inflammation in the body can trigger plaque formation.
Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease
Risk factors for CAD can be divided into two categories: modifiable and non-modifiable.
Modifiable risk factors include:
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet
- Excessive stress
Non-modifiable risk factors include:
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Gender (men have a higher risk before age 55, women after menopause)
- Family history of CAD
- Certain ethnicities (e.g., South Asians have a higher risk)
It is crucial to manage modifiable risk factors through lifestyle changes and appropriate medication to reduce the risk of CAD.
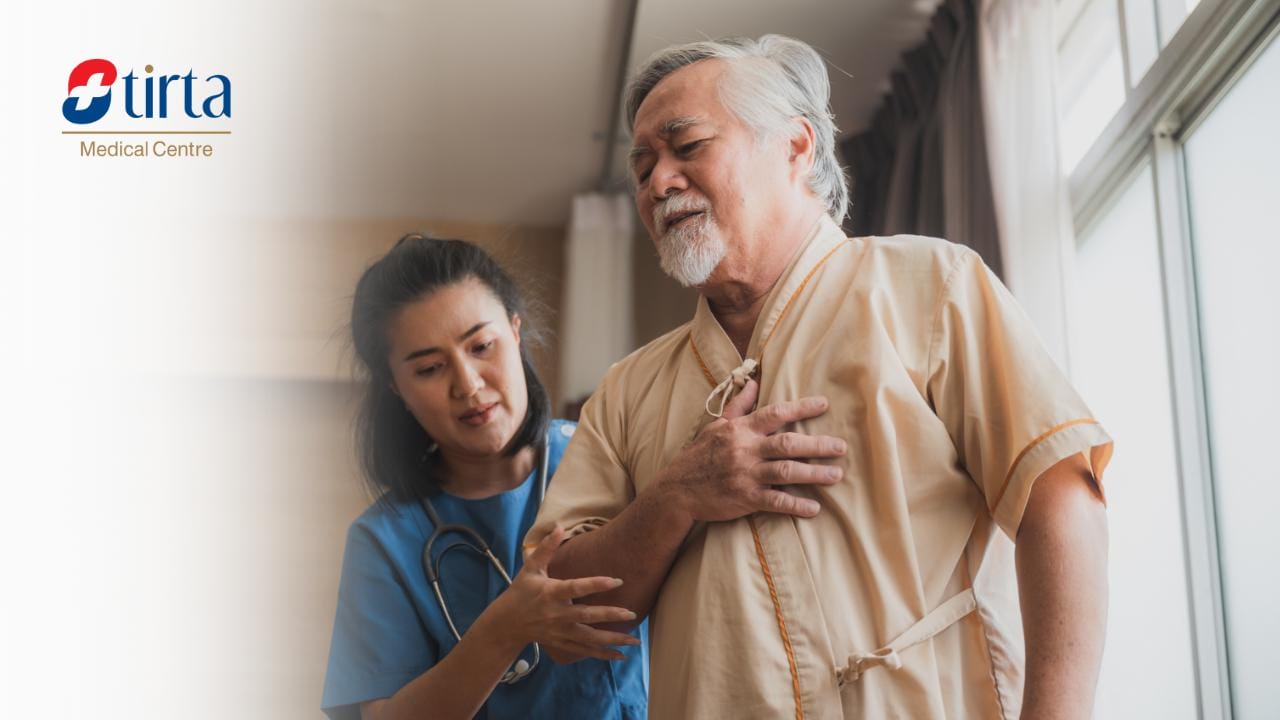
Coronary Heart Disease Symptoms
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) symptoms can differ from person to person and may not show up until a heart attack happens. Some symptoms of coronary heart disease include:
1. Angina
Pain or discomfort in the chest that may feel like pressure, burning, or tightness. Angina can spread to the left arm, neck, jaw, or back.
2. Shortness of Breath
Especially during physical activity or when lying down.
3. Palpitations
Rapid, pounding, or irregular heartbeats.
4. Unusual Fatigue
Particularly during activities that are typically manageable.
5. Nausea or Vomiting
Especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain.
6. Dizziness or Fainting
Especially during physical activity.
7. Cold Sweat
Often accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain.
It’s important to note that CHD symptoms in women may differ and are often more subtle compared to men. Women may more frequently experience symptoms like back, jaw, or neck pain, as well as nausea and unusual fatigue.
If you experience these symptoms, especially if they last for more than a few minutes or occur repeatedly, seek medical help immediately. Early detection and management are crucial in managing CHD.
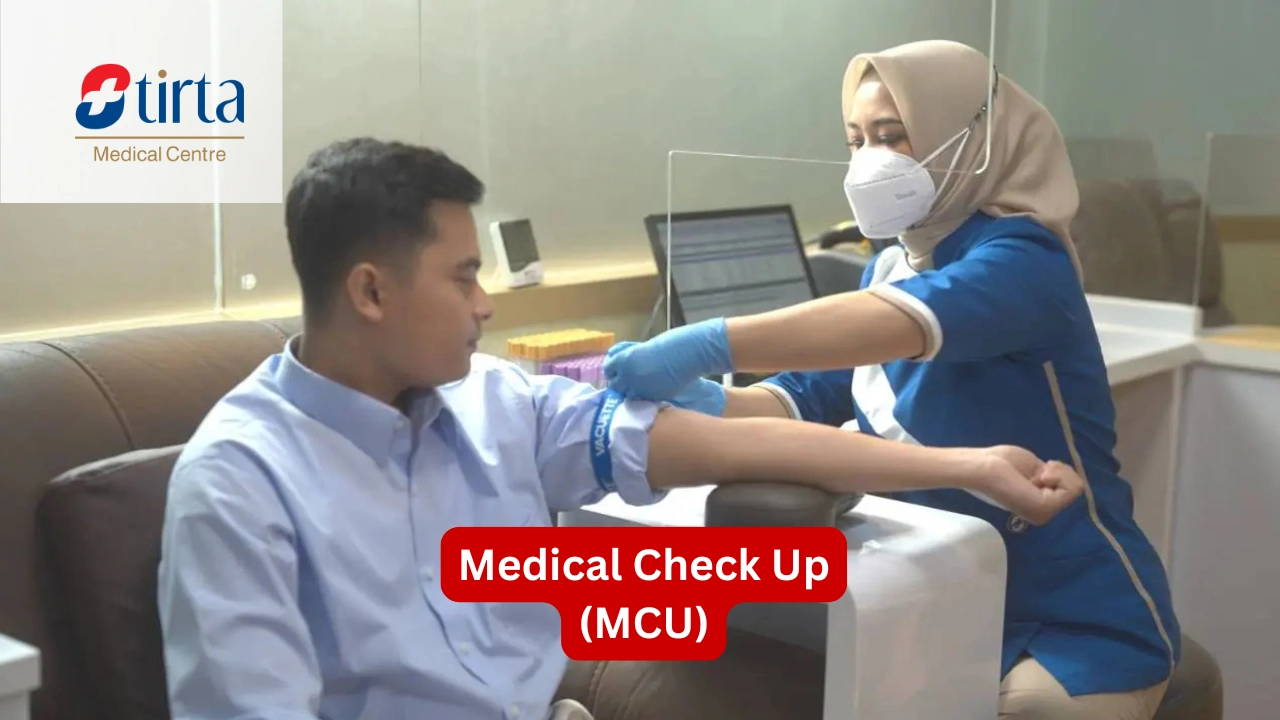
Diagnosis of Coronary Heart Disease
Diagnosing coronary heart disease involves several steps, starting with a complete physical examination and medical history. Doctors will ask about symptoms, family health history, and potential risk factors the patient may have.
Some diagnostic tests that may be conducted include:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) to record the heart’s electrical activity.
- Stress Test to evaluate how the heart performs during physical activity.
- Echocardiogram using sound waves to image the heart structure.
- Coronary Angiography is an imaging procedure that uses contrast material and X-rays to view blood flow through the coronary arteries.
- Heart CT Scan to provide detailed images of the heart structure and blood vessels.
- Blood Tests to measure cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and other heart markers.
Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
Treatment for coronary heart disease aims to reduce symptoms, slow disease progression, and prevent complications such as heart attacks. Treatment strategies for coronary heart disease include:
1. Lifestyle Changes:
- Quitting smoking
- Adopting a healthy diet
- Increasing physical activity
- Managing stress
2. Medications:
- Aspirin to prevent blood clots
- Statins to lower cholesterol levels
- Beta-blockers to lower blood pressure and heart rate
- ACE inhibitors to control blood pressure
- Nitrates to relieve chest pain
3. Medical Procedures:
- Angioplasty and stent placement to open blocked arteries
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a surgery to reroute blood flow around blocked arteries
Coronary Heart Disease Prevention
Preventing coronary heart disease is crucial and can be achieved by adopting a healthy lifestyle. Some preventive steps for coronary heart disease include:
- Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke.
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Engaging in regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes per week).
- Maintaining an ideal body weight.
- Effectively managing stress.
- Controlling cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and blood sugar.
- Limiting alcohol consumption.
Coronary Heart Disease Complications
If not properly managed, coronary heart disease can lead to several serious complications, including:
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmia
- Sudden Cardiac Death
- Aortic aneurysm
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
When to See a Doctor?
It is important to seek medical help immediately if you experience symptoms that may indicate heart problems. Contact emergency services or visit the nearest clinic, such as Tirta Medical Centre, if you experience:
- Severe chest pain lasting more than a few minutes
- Sudden and severe shortness of breath
- Dizziness or fainting
- Very fast or irregular heartbeats
Getting help early can prevent serious problems and improve life for patients with coronary heart disease.
Increased awareness of coronary heart disease aims to help the public recognize its risk factors and early symptoms. Early prevention and management are crucial to reducing the burden of coronary heart disease in Indonesia.
FAQ
Coronary heart disease cannot be completely cured, but it can be well-managed through lifestyle changes and appropriate treatment. Effective management can help individuals with CHD reduce symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance their quality of life.
Effective management of coronary heart disease (CHD) involves controlling risk factors, using medication, and sometimes performing procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
What Are the Restrictions for Coronary Heart Disease Patients?
Individuals with CHD should avoid the following to maintain heart health:
– Foods high in saturated and trans fats
– High-salt foods
– Processed and fast foods
– Excessive alcohol consumption
– Smoking and exposure to tobacco smoke
– Excessive stress
– Sedentary lifestyle
– Foods high in sugar and processed carbohydrates Patients should consult with a doctor for dietary and lifestyle guidance tailored to their individual conditions.
References:
- P2PTM Kemenkes. Accessed in 2024. What Are the Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)?: https://p2ptm.kemkes.go.id/infographic/apa-saja-faktor-risiko-penyakit-jantung-koroner-pjk
- Kulon Progo Health Office. Accessed in 2024. Coronary Heart Disease: https://dinkes.kulonprogokab.go.id/detil/181/penyakit-jantung-koroner
- Kemenkes Ditjen Yankes. Accessed in 2024. Management of Coronary Heart Disease: Surgery or PCI?: https://yankes.kemkes.go.id/view_artikel/3275/penanganan-penyakit-jantung-koroner-operasi-atau-pci
- RSUD Dr. Iskak Tulungagung. Accessed in 2024. Bad Habits That Trigger Coronary Heart Disease: https://rsud.tulungagung.go.id/kebiasaan-buruk-yang-memicu-penyakit-jantung-koroner/
- RSUD Talisayan, Berau Regency. Accessed in 2024. Recognize the Symptoms of Coronary Heart Disease: https://rsudtalisayan.beraukab.go.id/detail/kenali-gejala-penyakit-jantung-koroner
- RSUD Cilacap. Accessed in 2024. Coronary Heart Disease and Its Prevention: https://rsud.cilacapkab.go.id/v2/penyakit-jantung-koroner-dan-pencegahannya/
- NHLBI, NIH. Accessed in 2024. Coronary Heart Disease – What Is Coronary Heart Disease: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/coronary-heart-disease
- Mayo Clinic. Accessed in 2024. Coronary Artery Disease – Symptoms and Causes: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350613
- American Heart Association. Accessed in 2024. Coronary Artery Disease – Coronary Heart Disease: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiovascular-disease/coronary-artery-disease
- Healthline. Accessed in 2024. Coronary Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments: https://www.healthline.com/health/coronary-artery-disease
- WebMD. Accessed in 2024. What Is Coronary Artery Disease? Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention: https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/coronary-artery-disease