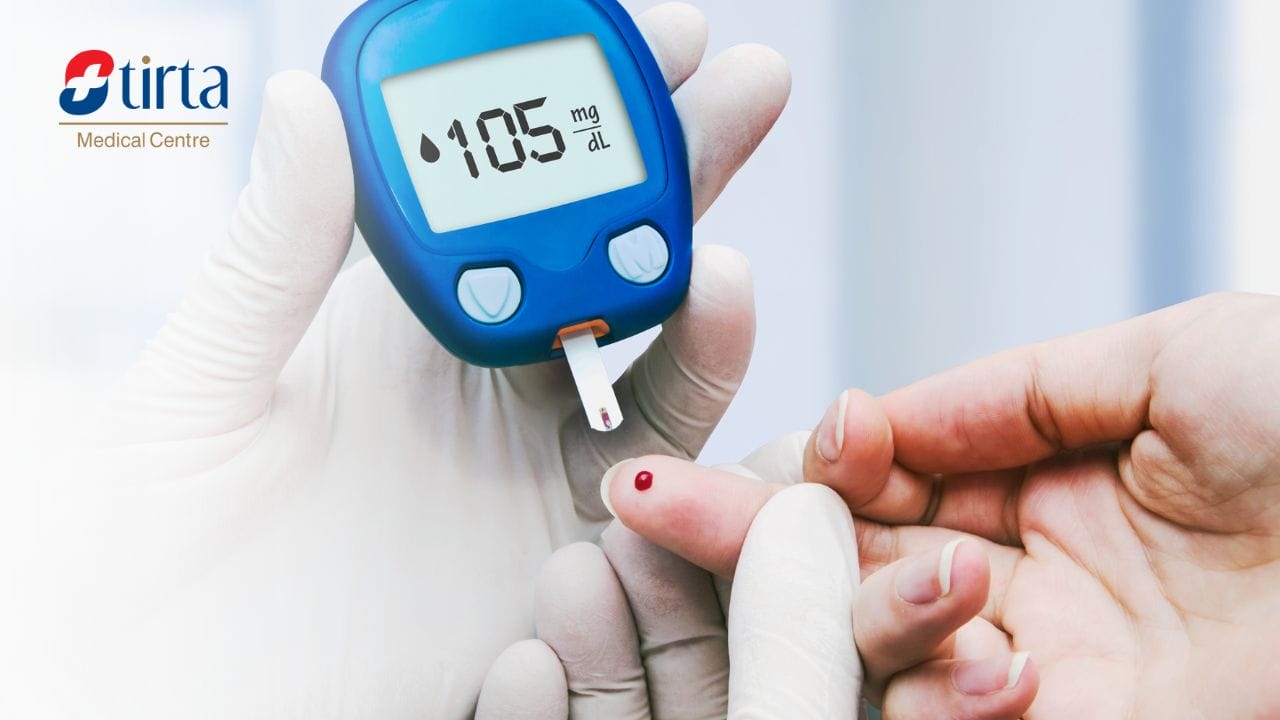
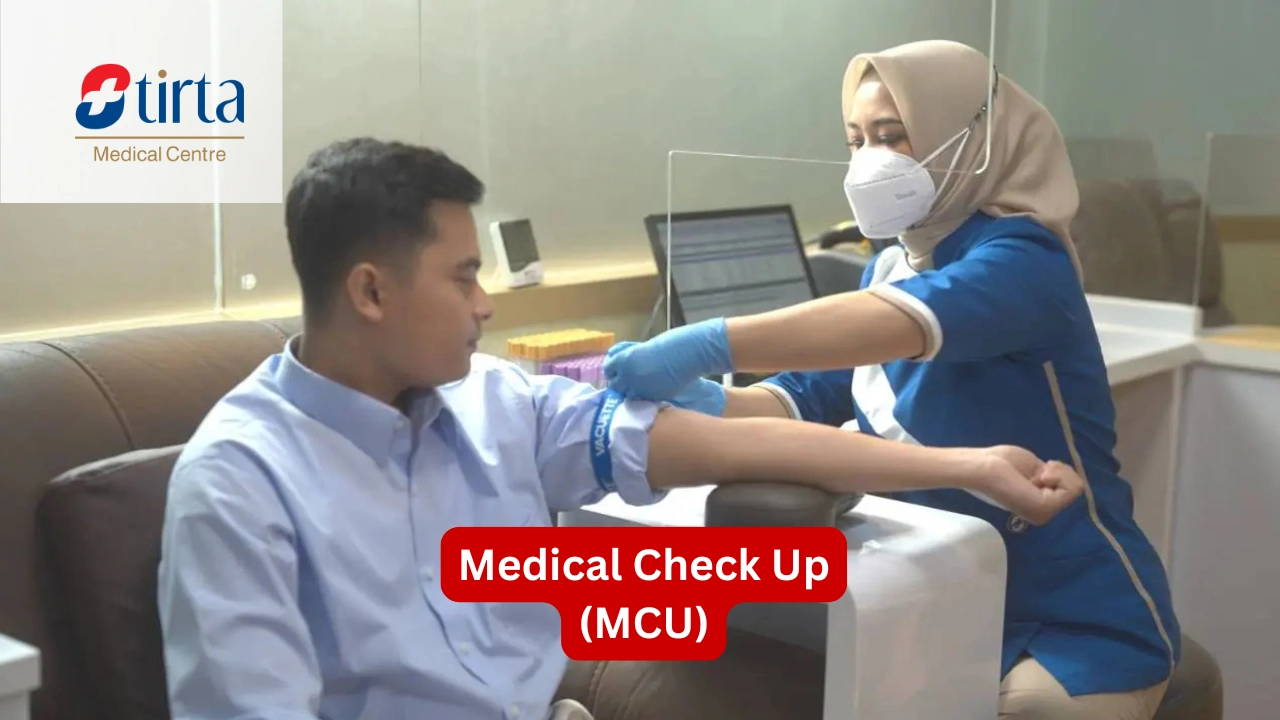
Understanding the importance of blood glucose tests is the first step in effectively preventing and managing diabetes. This test helps detect blood glucose levels and is important for monitoring the health of diabetes patients.
What is Blood Glucose Test?
Blood glucose test is a laboratory examination performed to measure the glucose (sugar) levels in the blood. It is a key method for diagnosing, monitoring diabetes, and assessing treatment effectiveness.
Glucose is the main energy source for body cells. Its level in the blood is regulated by the hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas. In diabetes patients, there is a disturbance in the production or function of insulin, leading to uncontrolled blood glucose levels.
Blood glucose tests can be conducted through venous blood sampling at a laboratory or using a portable glucose meter (glucometer). The glucometer uses a capillary blood sample taken from the fingertip.
Regular blood glucose tests is crucial for diabetes patients to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and prevent complications.
The doctor decides the testing frequency based on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and the patient’s blood glucose control.
Types of Blood Glucose Tests
There are several common types of blood glucose tests used to diagnose and monitor diabetes mellitus:
1. Random Blood Sugar (RBS)
This test can be performed at any time without special preparation. RBS measures the blood glucose level at the time of sample collection, regardless of the last meal time.
2. Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS)
This test is conducted after fasting for 8-10 hours. FBS provides an overview of the basal blood glucose level and is used to diagnose diabetes.
3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
OGTT involves measuring fasting blood sugar, then the patient is asked to drink a 75-gram glucose solution. Blood sugar is measured again 2 hours later to assess the body’s response to the glucose load.
4. Two-Hour Postprandial Glucose (2HPP):
This test is done 2 hours after eating to check how well the body manages sugar levels after a meal.
5. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
HbA1c reflects the average blood sugar level over the last 2-3 months. This test does not require fasting and is very useful for monitoring long-term diabetes control.
Benefits of Blood Glucose Tests
Routine blood glucose tests offers various important benefits:
1. Early Detection of Diabetes
Blood glucose tests enables the early detection of diabetes or prediabetes, allowing for early intervention to prevent complications.
2. Evaluation of Treatment Effectiveness
For diabetes patients, regular testing helps monitor treatment success and any needed changes in medication or insulin dosages.
3. Prevention of Complications
Carefully tracking blood sugar levels can prevent or slow the progression of diabetes complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
4. Optimization of Diabetes Management
Blood glucose tests results assist in adjusting diet, physical activity, and medication to achieve optimal glycemic control.
5. Increased Awareness and Motivation
Routine testing enhances patient awareness of the importance of diabetes control and motivates them to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
6. Identification of Risk Factors
Blood glucose tests can identify individuals at high risk of diabetes, allowing for early intervention to prevent disease progression.
7. Adjustment of Treatment Plans
Doctors can tailor treatment plans based on blood glucose test results to achieve desired control targets.
Blood glucose tests are a crucial component in comprehensive diabetes management. Consult with your doctor to determine the appropriate types and frequency of testing based on your health condition.
Diseases Caused by High Blood Sugar
Long-term high blood sugar levels can cause various serious complications such as:
- Coronary heart disease
- Stroke
- Chronic kidney failure
- Diabetic retinopathy (damage to the retina of the eye)
- Diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Diabetic ulcers
- Sexual dysfunction
When is Blood Glucose Testing Necessary?
Blood glucose testing is a critical component in diabetes management and early detection of metabolic diseases. Here are situations when one should undergo blood glucose testing:
1. Diabetes Diagnosis
Blood glucose testing is necessary to diagnose diabetes mellitus. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends diabetes screening for adults aged 45 and above or those with diabetes risk factors.
2. Routine Diabetes Monitoring
Diabetes patients need to undergo regular blood glucose testing to monitor treatment effectiveness and disease control. The frequency of testing varies depending on the type of diabetes and treatment regimen.
3. Pregnancy
Pregnant women should undergo the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy to screen for gestational diabetes.
4. Symptoms of Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia
Blood sugar testing is important when someone has symptoms of high blood sugar (like frequent urination, increased thirst, weight loss) or low blood sugar (like heart palpitations, sweating, shaking).
5. Medication Adjustments
Doctors may suggest testing blood sugar levels more often when the diabetes treatment or insulin dosage changes.
6. Acute Illness or Stress
People with diabetes should check their blood sugar more often when they are sick or stressed, as these can change blood sugar levels.
7. Before and After Intense Physical Activity
Blood glucose testing before, during, and after exercise can help prevent complications of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia in diabetes patients.
Blood Glucose Testing Procedures
Blood glucose testing can be conducted using several methods:
1. Capillary Blood Glucose Test (Finger Prick Test)
- Wash hands with soap and warm water, then dry them.
- Prepare the glucometer and test strip.
- Use a sterile lancet to prick the fingertip.
- Apply a drop of blood onto the test strip.
- Insert the test strip into the glucometer.
- Read the result displayed on the glucometer screen.
2. Venous Blood Glucose Test
- Conducted by healthcare professionals.
- Patients are asked to fast for 8-10 hours (for Fasting Blood Sugar, FBS) or 2 hours after eating (for 2-Hour Postprandial Blood Sugar, 2HPP).
- Blood is drawn from a vein in the arm using a syringe.
- The blood sample is sent to the laboratory for analysis.
3. HbA1c Test
- Does not require fasting.
- Blood is drawn from a vein.
- The sample is analyzed in the laboratory using chromatography or immunoassay methods.
- Results reflect the average blood sugar levels over the last 2-3 months.
4. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
- A small sensor is placed under the skin, usually on the abdomen or upper arm.
- The sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid every few minutes.
- Data is transmitted to a receiver device or smartphone.
- Provides information on glucose trends throughout the day and night.
The choice of blood glucose testing method depends on the purpose of the test, patient’s condition, and doctor’s recommendation. It is important to follow the preparation instructions and procedures provided by healthcare professionals to ensure accurate results.
Cost of Blood Glucose Testing at Tirta Medical Centre (TMC)
Prices for blood glucose tests can differ based on the test type, location, and healthcare provider. Here are the prices for various types of blood glucose tests at Tirta Medical Centre:
- Cost for Random Blood Sugar (RBS) test is around IDR 40,000.
- Cost for Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) test is around IDR 40,000.
- Cost for 2-Hour Postprandial Glucose (2HPP) test is around IDR 40,000.
- Cost for HbA1c test is around IDR 185,000.
- Cost for a diabetes testing package is around IDR 595,000.
Note: The price range can change at any time. Friends of Tirta can contact us for price updates or make a reservation directly here:
Blood Glucose Test Results
Interpreting blood glucose test results is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes mellitus. Here is a general guide to understanding blood glucose test results:
1. Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS):
- Normal: < 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100-125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 126 mg/dL
2. Two-Hour Postprandial Blood Sugar (2HPP):
- Normal: < 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 140-199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 200 mg/dL
3. Random Blood Sugar (RBS):
- Normal: < 200 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 200 mg/dL (if accompanied by classic symptoms of diabetes)
4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
- Normal: < 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 140-199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 200 mg/dL
5. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c):
- Normal: < 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% – 6.4%
- Diabetes: ≥ 6.5%
For type 2 diabetes patients who are already diagnosed, the recommended blood sugar control targets are:
- HbA1c: < 7.0% for most adults
- FBS: 80-130 mg/dL
- 2HPP: < 180 mg/dL
However, these targets can be adjusted based on age, duration of diabetes, comorbidities, and other individual risk factors. Some patients may require tighter or looser targets depending on their clinical condition.
Blood glucose test results should always be interpreted by a doctor considering the patient’s overall health. An isolated abnormal test result does not automatically indicate a diabetes diagnosis, just as normal results do not assure that an individual is free from the risk of developing diabetes.
Best Place for Blood Glucose Testing at Tirta Medical Centre
Tirta Medical Centre provides comprehensive blood glucose testing services with high-quality standards, already included in the Medical Check-Up Package. The available facilities include:
- Modern technology laboratories
- Experienced medical staff and analysts
- Quick and accurate test results
- General practitioner or internal medicine specialist consultations
- Comprehensive diabetes testing packages
Tirta Medical Centre is strategically located with more than 30 branches across Indonesia and offers flexible operating hours.
For more information or to make an appointment, Friends of Tirta can contact us here:
Routine blood glucose testing is essential for early detection of diabetes and preventing complications. Consult with your doctor about a suitable testing schedule based on your health condition.
References:
- UNHAS Journal. Accessed in 2024. Achievement of Glycemic Targets and Analysis of Related Factors in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: https://journal.unhas.ac.id/index.php/mff/article/download/13037/7273/53975
- Stikes Yayasan RS Dr. Soetomo Journal. Accessed in 2024. The Effect of 5 Hours and 10 Hours of Storage at 2-8 °C on Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Levels: https://jurnal.stikes-yrsds.ac.id/index.php/JMK/article/view/162
- Institute for Research and Community Services, Universitas Muhammadiyah Palangkaraya. Accessed in 2024. HbA1c Levels in Female Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at RSUD dr. Doris Sylvanus Palangka Raya: https://journal.umpr.ac.id/index.php/bjmlt/article/download/1086/984/4190
- UNAIR. Accessed in 2024. The Importance of Self-Checking Blood Glucose and HbA1c Levels in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: https://unair.ac.id/pentingnya-cek-mandiri-kadar-gula-darah-dan-hba1c-pada-anak-diabetes-melitus-tipe-1/
- American Diabetes Association. Accessed in 2024. Understanding A1C Test: https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes/a1c
- Healthline. Accessed in 2024. What Are the Different Types of Diabetes?: https://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes/types-of-diabetes
- WebMD. Accessed in 2024. Hemoglobin: A1C Test, Range, and Normal Levels: https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/glycated-hemoglobin-test-hba1c
- Medical News Today. Accessed in 2024. Fasting Blood Sugar (Glucose): Normal Levels and Testing: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317466
- CDC. Accessed in 2024. Testing for Diabetes and Prediabetes: A1C: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/diabetes-testing/prediabetes-a1c-test.html
- Mayo Clinic. Accessed in 2024. Diabetes – Diagnosis and Treatment: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20371451
- CDC. Accessed in 2024. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/diabetes-testing/monitoring-blood-sugar.html
- MedlinePlus. Accessed in 2024. Blood Glucose Test: https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/blood-glucose-test/
- WebMD. Accessed in 2024. Blood Sugar Test: How and When to Get It Done: https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/how-test-blood-glucose