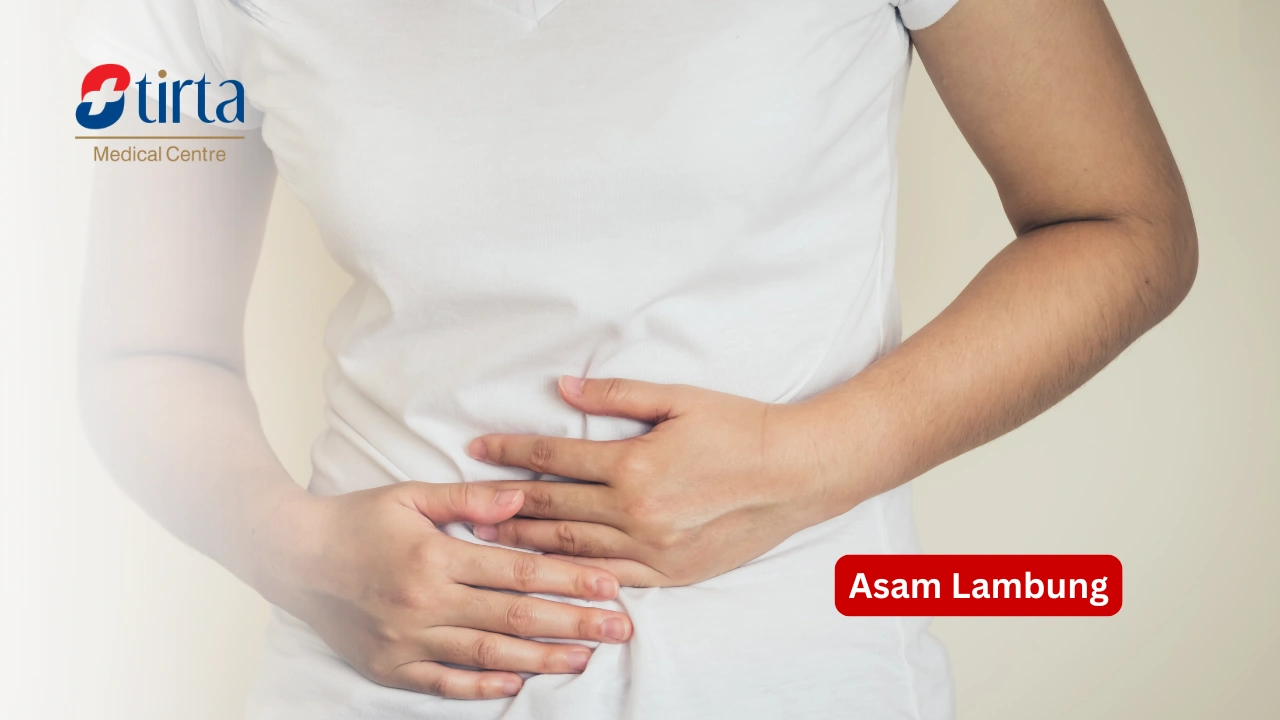
When acid reflux occurs, it can disrupt various activities being carried out. You may feel nauseous, have a burning sensation in your throat, stomach pain, and a bitter taste in your mouth.
Acid reflux can be caused by various factors such as recently eaten food, lack of sleep, or stress. If not treated promptly, it can lead to quite serious health issues.
This article will discuss how to manage acid reflux. We will start by explaining what acid reflux is, its causes, and risk factors.
Definition of Acid Reflux
Acid reflux disease, commonly known as Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), is a condition where stomach acid rises into the esophagus. This condition can cause heartburn and various other symptoms in the lower chest and stomach area.
Most people with this disease have mild acid reflux at least twice a week and more severe symptoms at least once a week.
It’s important for people with acid reflux to know how to reduce symptoms. This can be done by making lifestyle changes or taking medications.
Causes of Acid Reflux
There are various causes that lead to acid reflux disease:
- Certain types of food, such as dairy, spicy or fried foods, and poor eating habits.
- Obesity.
- Certain medications such as asthma drugs, high blood pressure and allergy medications, painkillers, sedatives, and antidepressants.
- Pregnancy, due to too much pressure on the stomach.
- Old age.
- Suffering from scleroderma, a disease that attacks connective tissues.
- Hiatal hernia occurs when the top part of the stomach and the sphincter move above the diaphragm, which is the muscle separating the stomach from the chest. The diaphragm normally helps keep stomach acid in place. However, in this condition, the acid can go up to the esophagus and cause symptoms of acid reflux.
- Experiencing gastroparesis, a condition where the stomach muscles are weakened, causing slow stomach emptying.
Symptoms of Acid Reflux Disease
Acid reflux disease can cause an uncomfortable burning sensation in the chest that can even spread to the neck. This can get worse in acid reflux sufferers when lying down or bending over.
Acid reflux disease causes symptoms that can last for hours and worsen after eating. You may have a sour or bitter taste in your mouth or vomit food or liquid from your stomach. GERD symptoms can also cause difficulty swallowing.
Additionally, this disease can cause respiratory issues such as chronic cough or asthma. Other symptoms include:
- Sour or bitter taste at the back of the mouth
- Difficulty or pain swallowing
- Excessive saliva production
- Chronic sore throat
- Hoarseness
- Gum inflammation
- Bad breath
- Chronic cough
- Tooth damage
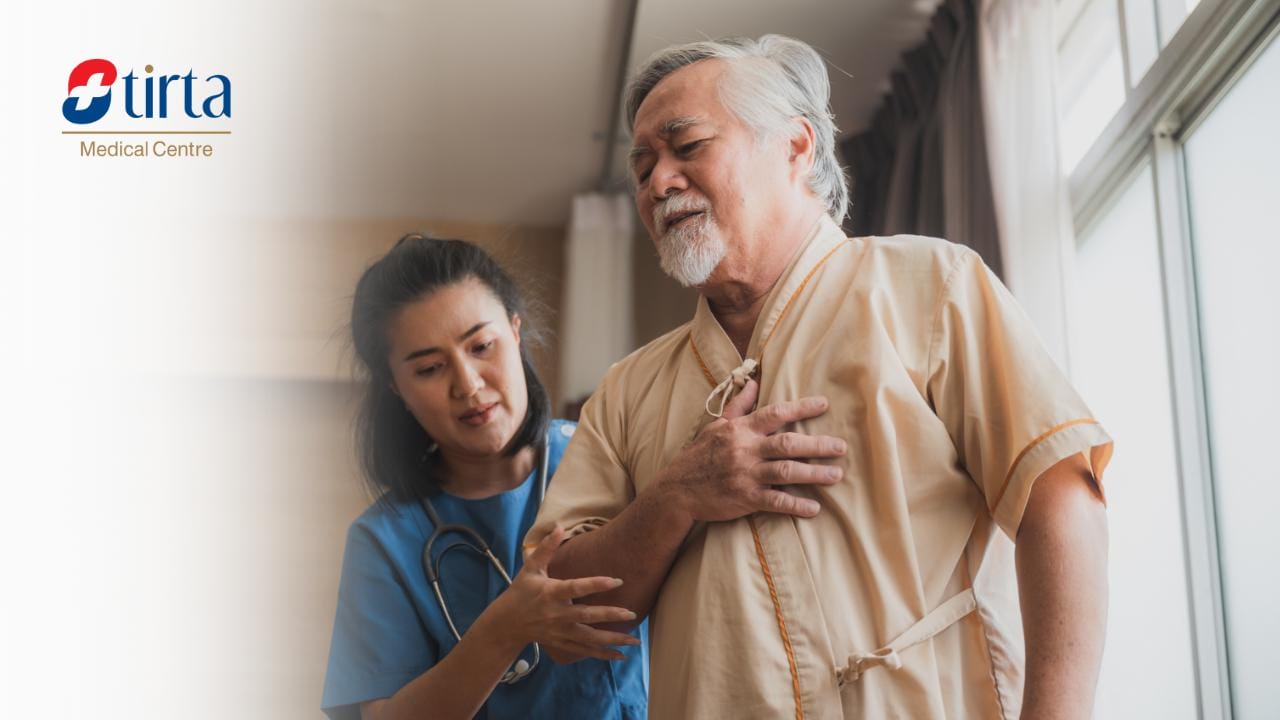
- Chest pain (seek immediate help)
Babies and children may experience almost the same symptoms as acid reflux:
- Frequent small vomits.
- Breathing difficulties.
- Excessive crying, refusing to eat.
- Difficulty sleeping after eating, especially in babies.
- Choking while sleeping, which can wake the child.
- Hoarse throat.
- Bad breath.
How to Overcome Acid Reflux
Managing acid reflux or GERD can be achieved through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgery. Here is a complete explanation:
1. Lifestyle Changes
To alleviate acid reflux symptoms, doctors will first recommend lifestyle changes, such as:
- Losing weight if overweight.
- Eating smaller but more frequent meals.
- Avoiding foods and drinks that cause acid reflux, like caffeine and alcohol.
- Limiting or reducing the consumption of certain medications like aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Not bending over, reclining, or lying down for at least 3 hours after eating.
- Sleeping in a position with additional pillows to elevate the body from the waist up.
- Avoiding tight clothing.
- Not smoking.
2. Medications
Several medications can be taken to alleviate acid reflux symptoms, including:
1. Medications That Inhibit Stomach Acid Production
Proton pump inhibitors (such as lansoprazole or omeprazole) can be used to reduce acid production and promote healing of the esophageal tissue.
2. Medications that Neutralize Stomach Acid
Antacids containing calcium carbonate can neutralize stomach acid and quickly relieve acid reflux symptoms. Overuse of antacids may cause side effects such as diarrhea and kidney issues.
3. Medications that Reduce Acid Production
By reducing acid production, inflammation in the esophagus can also improve. Examples include H2 antagonists (e.g., cimetidine, famotidine, or ranitidine). Unlike antacids that neutralize stomach acid immediately, these medications work slower but provide longer relief.
3. Surgery
Surgery is the last resort in treating acid reflux, especially if lifestyle changes and medications are ineffective. Surgery is recommended for patients with complications such as narrowing of the esophagus, which makes it hard for food to pass into the stomach. Several types of surgeries can be performed, including:
1. Fundoplication or LES Muscle Banding Surgery
This surgery aims to prevent acid reflux by wrapping the top of the stomach around the LES (Lower Esophageal Sphincter) muscle.
2. LINX Device Surgery
A ring-shaped magnetic device is wrapped around the LES muscle area to prevent acid reflux while still allowing food and drinks to pass through.
Successfully Treating Acid Reflux?
These are some things you need to know about acid reflux. There are several lifestyle changes you can try and some medications you can take. If it becomes severe, surgery is also a solution you can consider.
If you need online consultation, you can consult online with Tirta Medical Centre. Consult your condition with experienced and certified doctors. Contact Tirta Medical Centre for more detailed information. You can also purchase medication online without leaving your home.
FAQ
Acid reflux can also occur in babies, usually because the LES (Lower Esophageal Sphincter) muscle is still developing. Symptoms of acid reflux in babies include burping or regurgitation after eating or nursing. It is important to be cautious if symptoms persist after the child is one year old.
2. When Should You See a Doctor for Acid Reflux?
If you have tried changing your lifestyle and taking certain medications but experience worsening symptoms, it is best to contact a doctor for further treatment.
To diagnose acid reflux, the doctor will perform an anamnesis, including risk factors. The doctor will then conduct a physical examination on the patient and some additional diagnostic steps. Further examinations that can be performed include Electrocardiogram (ECG), Gastroscopy, Esophageal Manometry, X-rays, and Esophageal pH Measurement.
Although not fatal, acid reflux needs to be treated to prevent complications.
– Oatmeal
– Watermelon
– Plant-based Milk
– Low-fat Milk
– Ginger Tea
– Coconut Water
– Fruit juices like citrus or apple.
Reference:
- Slater, B., et al. (2021). SAGES Guidelines for the Surgical Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD). Surgical Endoscopy, 35(9), pp. 4903–17.
- Harris, J., et al. (2022). Clinical Practice Guidelines on Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Quality Appraisal of International Guidelines. Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition, 25(2), pp. 109.
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology (2019). Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
- American Gastroenterological Association (2021). Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
- National Institute of Health (2020). The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease. Acid Reflux (GER and GERD) in Adults.
- Mayo Clinic (2020). Disease & Conditions. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.
- Hoffman, M. WebMD (2021). Heartburn Surgery.